Scaling email volume is tricky – push too fast, and you risk spam filters or domain blacklists. Move too slow, and you miss growth opportunities. Here’s the key: gradual, consistent scaling protects your sender reputation and ensures your emails land in inboxes.
Key Takeaways:
- Warm up mailboxes and domains: Start small (3–10 emails/day) and increase volume weekly.
- Set limits: Keep daily sends per mailbox at 30–50 emails for cold outreach.
- Distribute volume: Use multiple mailboxes and domains to avoid flagging by email providers.
- Monitor metrics: Bounce rates under 1%, spam complaints below 0.1%, and open rates above 15% are critical.
- Focus on list quality: Remove inactive contacts and prioritize engaged recipients.
Scaling email isn’t about volume – it’s about trust. Gradual increases, clean lists, and consistent engagement are your best tools to succeed. Let’s dive into the details.
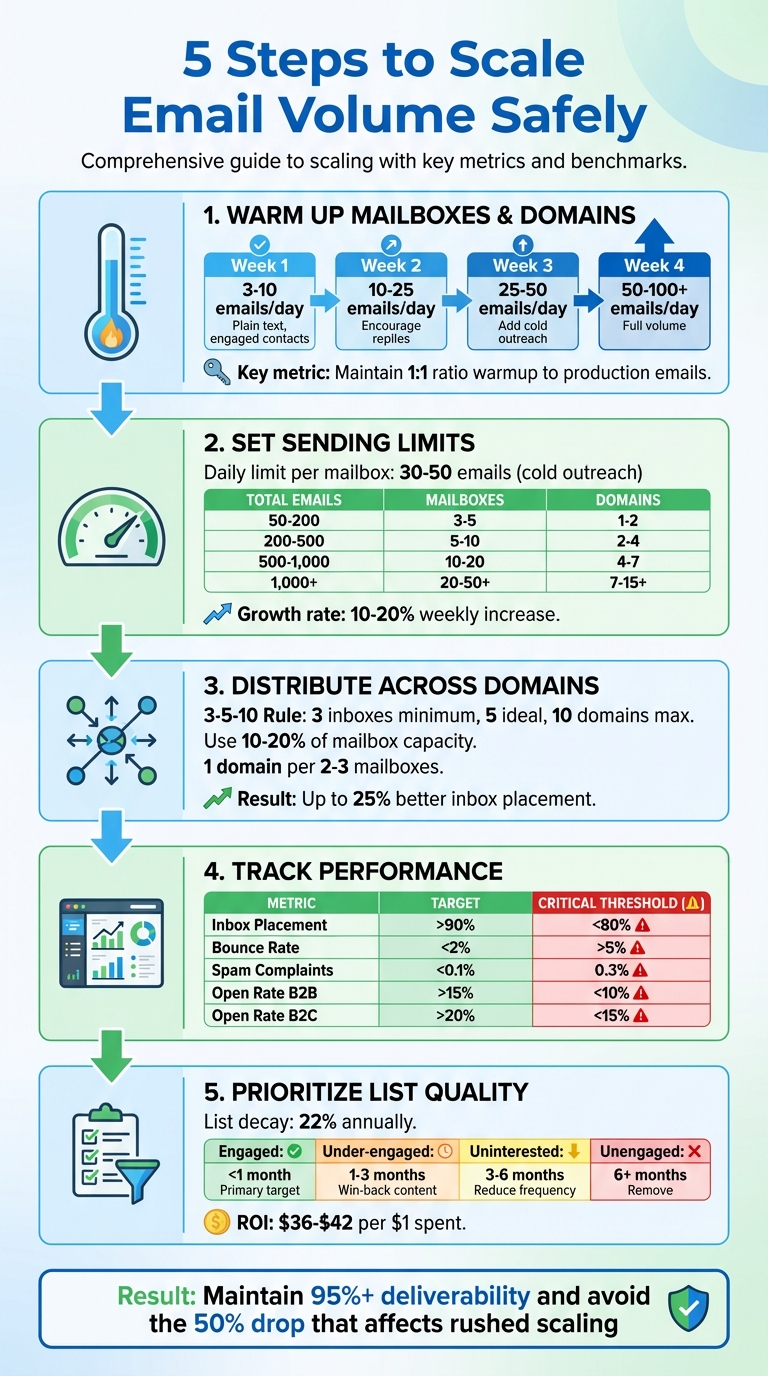
5-Step Email Volume Scaling Process with Key Metrics and Benchmarks
How to Scale to 100K Emails/Month Without Killing Deliverability
Step 1: Warm Up Your Mailboxes and Domains
Before scaling your email outreach, it’s crucial to establish credibility. A new domain lacks history – essentially, it has no "digital credit score" – so major email providers often view it with suspicion. If you send too many emails too quickly, spam filters will likely flag you before you even get off the ground.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to warming up your mailbox and domains to ensure a smooth transition to higher volumes.
How to Warm Up a Mailbox
Start by sending a small number of emails and gradually increase the volume over time. Below is a week-by-week breakdown of an effective warmup schedule:
| Phase | Daily Volume (Per Mailbox) | Focus/Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | 3–10 emails | Plain text; send to highly engaged contacts |
| Week 2 | 10–25 emails | Continue conversations; encourage replies |
| Week 3 | 25–50 emails | Add cold outreach if metrics remain positive |
| Week 4 | 50–100+ emails | Scale to full volume; keep patterns consistent |
In Week 1, stick to plain-text emails and send them to trusted, high-reputation contacts. This mimics natural, human email behavior.
By Week 2, aim to spark engagement by encouraging recipients to reply, star your messages, or mark them as "not spam." Two-way interactions signal to email providers that your activity is legitimate.
In Week 3, if your bounce rate is under 1% and spam complaints are nearly zero, you can begin introducing cold outreach emails. Be sure to maintain a healthy balance between warmup and cold emails.
By Week 4, your mailboxes should be ready to handle your target volume – typically 30 to 50 emails per day per inbox for Gmail and Microsoft accounts. At this stage, keep a 1:1 ratio of warmup to production emails to maintain credibility.
Important Tip: Avoid using public link shorteners like bit.ly or tinyurl during the warmup phase. These are often flagged by spam filters. If your emails start landing in Gmail’s "Promotions" or "Spam" tabs, reduce your sending volume by 25% and focus only on highly engaged recipients until your metrics recover.
Next, let’s explore how pre-warmed mailboxes can simplify this process and protect your primary domain.
Using Pre-Warmed Mailboxes to Save Time
Manually warming up mailboxes is effective, but it’s also time-intensive and challenging to scale. If you’re managing multiple mailboxes or need to scale quickly, pre-warmed infrastructure can significantly speed up the process.
Pre-warmed mailboxes come from aged domains with established sender reputations. This means you can avoid the "high-risk" scrutiny that new domains typically face. Instead of starting from scratch, you’re leveraging mailboxes with a history of positive engagement.
For example, Zapmail offers pre-warmed Google and Microsoft mailboxes designed for high deliverability. These accounts come pre-configured with essential authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, so you don’t need to handle the setup manually. With these mailboxes, you can start sending higher volumes right away, skipping the usual two-to-four-week warmup period required for new mailboxes.
Why it matters: Using pre-warmed secondary domains for outreach protects your main business domain. This ensures that any deliverability issues won’t affect your primary domain. As SkySenders puts it:
"Your domain is your identity. Burn it once, and recovery is hard".
Even with pre-warmed mailboxes, it’s essential to maintain strong engagement ratios and monitor performance closely to reach your full volume safely and efficiently.
Step 2: Set Daily and Weekly Sending Limits
Once your mailboxes are warmed up, it’s important to establish daily and weekly sending limits. These limits help protect your sender reputation and prevent overloading any single mailbox.
Recommended Sending Caps Per Mailbox
For cold outreach, aim for a daily volume of 30 to 50 emails per mailbox. This total includes both cold outreach and warmup emails. Stick to a 1:1 ratio – if you send 25 warmup emails, limit your cold emails to 25 as well.
After 4–6 weeks of warming up, some advanced systems can handle up to 200–300 emails daily. However, most users should keep their daily cap at 50 emails to avoid triggering spam filters.
Here’s a quick look at email limits for Google accounts:
- Google Workspace accounts: Up to 2,000 emails per day
- Personal Gmail accounts: Max of 500 emails per day
Daily Email Volume Recommendations:
| Daily Email Volume Goal | Recommended Number of Mailboxes | Recommended Number of Domains |
|---|---|---|
| 50–200 emails | 3–5 mailboxes | 1–2 domains |
| 200–500 emails | 5–10 mailboxes | 2–4 domains |
| 500–1,000 emails | 10–20 mailboxes | 4–7 domains |
| 1,000+ emails | 20–50+ mailboxes | 7–15+ domains |
To protect your domain’s reputation, limit total emails per domain to 2,000–5,000 daily. If higher volume is needed, add more domains instead of overloading existing ones.
Why Consistent Sending Patterns Matter
Email providers like Gmail and Outlook reward steady, predictable sending behaviors. Sudden spikes – like sending 1,000 emails after several days of inactivity – can trip spam filters or even lead to account suspensions.
Hans Dekker, a deliverability expert at Instantly.ai, emphasizes the importance of gradual scaling:
"Slow ramp warmup is the deliberate act of starting with a small number of emails from a mailbox or domain and increasing volume in steady steps over time. The goal is to look like a real sender".
To appear natural, avoid sending hundreds of emails at the same time every day. Instead, spread them out. For example, if your target is 500 emails daily, send about 50 emails per hour over a 10-hour window.
When increasing volume, stick to a 10–20% weekly growth rate as long as:
- Bounce rates stay under 1%
- Spam complaints remain below 0.1%
If open rates drop below 15–20%, pause scaling and reassess your content or list quality. Erratic sending patterns or sudden bursts can raise red flags, but steady, consistent behavior helps maintain a positive sender reputation.
How to Calculate Your Volume Requirements
To figure out how many emails you need to send, work backward from your sales goals. Here’s the formula:
Total monthly emails = (Sales target ÷ Close rate from replies) ÷ Reply rate
For example, if your goal is to gain 10 customers per month with a 20% close rate and a 5% reply rate:
- 10 sales ÷ 0.20 = 50 replies needed
- 50 replies ÷ 0.05 = 1,000 emails per month
- 1,000 emails ÷ 30 days ≈ 33 emails per day
At 50 emails per day per mailbox, one mailbox would suffice. However, it’s smart to have 20–30% more mailboxes than your calculations suggest to handle unexpected spikes.
Monthly Scaling Example:
| Monthly Volume Target | Required Daily Sends | Estimated Mailboxes Needed (at 250/day) |
|---|---|---|
| 10,000 | 333 | 2 |
| 100,000 | 3,333 | 14 |
| 200,000 | 6,667 | 27 |
| 500,000 | 16,667 | 67 |
Improving inbox placement from 85% to 97% can make a significant difference. For a $10 million email-driven business, this improvement could mean an extra $1.4 million in annual revenue. Managing your email volume properly isn’t just about technical precision – it can directly impact your bottom line.
Once your sending limits are in place, the next step is distributing this volume across multiple mailboxes and domains to ensure your infrastructure remains secure.
Step 3: Spread Volume Across Multiple Mailboxes and Domains
After setting your sending limits, the next step is to distribute your email volume across multiple mailboxes and domains. This approach acts like a "firewall", shielding your primary domain and improving your email deliverability.
How to Distribute Sends Across Mailboxes
To avoid being flagged as a bulk sender, spread your emails across several mailboxes. Sending a high volume from one account increases the risk of being flagged by ISPs. By rotating your sends across multiple accounts, you create a more natural and trusted email pattern that providers are less likely to penalize.
Here’s a practical tip: keep each mailbox at only 10–20% of its capacity. Research shows that sending far below a mailbox’s limit significantly improves inbox placement. For example, if you need to send 500 emails daily, use 10–15 mailboxes, each sending 30–50 emails, rather than overloading just a few accounts.
Stick to the 3-5-10 Rule for mailbox rotation: use at least three inboxes per domain, aim for five, and cap it at ten domains to keep things manageable. Additionally, maintain about one domain for every 2–3 mailboxes to avoid putting too much strain on any single domain’s reputation.
Hugo Pochet, Co-Founder of Mailpool, sums it up well:
"Instead of blasting all your emails from a single inbox, you rotate between different mailboxes to spread the sending volume and create more natural sending patterns that inbox providers trust".
To mimic organic email activity, use round-robin or time-staggered sending methods. This prevents any single account from being overused or flagged. Following these strategies can improve inbox placement by up to 25% and boost open rates by 15–20%. Without proper distribution, teams scaling quickly may see their deliverability plummet from 95% to below 50% within just a few months.
Next, consider using subdomains to further separate and manage your email streams.
Using Subdomains to Separate Email Types
Subdomains provide a way to isolate different types of emails, allowing ISPs to evaluate them independently. Instead of sending all emails from company.com, you can use subdomains like outreach.company.com for cold emails and t.company.com for transactional messages.
This separation is key because cold outreach often has lower engagement rates compared to transactional emails. Combining them on the same domain can harm your overall reputation, dragging down critical communications.
For cold outreach, consider using alternate domains like trycompany.com or getcompany.io. This creates a buffer for your primary domain, so if the outreach domain gets flagged, your main domain remains unaffected. To build trust, set up a permanent redirect from your outreach domains to your main website, allowing prospects to verify your brand’s legitimacy.
If you’re managing multiple clients or product lines, separate workspaces can help fully isolate risks. For long-term success, focus on strategic domain and mailbox rotation.
Rotating Domains and Mailboxes
Effective rotation involves more than just having multiple accounts – it’s about using them wisely. Rotate based on engagement, sending emails from your best-performing domains to your most engaged segments, while using "buffer" domains for riskier lists.
For advanced scaling, apply the 80/20 distribution rule: send 80% of your volume through your most reliable, established accounts, and the remaining 20% through newer or recovering accounts. This keeps your system stable while warming up new infrastructure.
If inbox placement drops below 85%, reduce your volume by 50% and focus on high-engagement segments for 7–14 days. This "quarantine" method helps isolate problems before they spread to your entire operation.
Engagement-based domain rotation can also reduce bounce rates by nearly 30%. Keep a close eye on each mailbox’s performance, and immediately remove underperformers from rotation. For added resilience, mix account types – such as Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 – to diversify your reputation risk.
Zapmail simplifies this process by offering pre-warmed mailboxes, automated DNS setup, and domain isolation. This tool saves time and effort, making it easier to scale without manual setup.
Danny Goff, Director of Sales at Propeller, highlights the benefits:
"Procedures that usually took hours (setting DKIM, SPF, etc. records) for multiple domains, now take a few minutes".
sbb-itb-36f7bf9
Step 4: Track Performance and Make Adjustments
After splitting your email volume across multiple mailboxes and domains, the next step is keeping a close eye on your performance metrics and making data-driven tweaks. Consistently monitoring deliverability signals is key to scaling safely and maintaining your email reputation. This stage builds on earlier steps like warming up and distributing your emails to ensure they continue landing where they should – your recipients’ inboxes.
Here’s a sobering fact: 21% of opt-in emails never make it to the inbox. However, email programs that actively track deliverability metrics see a 22% boost in campaign success compared to those that don’t.
Metrics to Monitor
Your focus should be on a handful of key metrics that reveal whether your emails are hitting inboxes or getting flagged. Start with the Inbox Placement Rate (IPR), which measures the percentage of emails making it to the primary inbox instead of spam. Top-performing senders aim for an IPR of 97.9%, so keeping yours above 90% is a good target.
Next, keep an eye on bounce rates, which fall into two categories:
- Hard bounces: Permanent issues like invalid email addresses.
- Soft bounces: Temporary problems such as full inboxes.
Hard bounce rates should stay below 2%; anything higher signals poor list quality and risks harming your sender reputation.
Spam complaint rates are another critical factor. These should remain under 0.1%, but note that providers like Google and Yahoo enforce stricter limits of 0.3%. Exceeding these thresholds can result in your emails being filtered out entirely.
Finally, monitor engagement metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and reply rates. For B2B campaigns, open rates below 15% are concerning, while for B2C, anything under 20% warrants a closer look.
Here’s a quick cheat sheet for benchmarks:
| Metric | Target Benchmark | Critical Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Inbox Placement | >90% | <80% |
| Bounce Rate | <2% | >5% |
| Spam Complaints | <0.1% | 0.3% (Google/Yahoo limit) |
| Open Rate (B2B) | >15% | <10% |
| Open Rate (B2C) | >20% | <15% |
To pinpoint issues, use ISP-specific tracking since deliverability can vary significantly between providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo. Tools such as Google Postmaster Tools and Microsoft SNDS offer valuable feedback from major email providers. For real-time insights, try seed list testing before and during scaling to confirm where your emails are landing.
How to Adjust Based on Data
When your metrics stray from the benchmarks, quick action is crucial. If performance falls below acceptable levels, pause your campaigns and investigate. Start by cleaning your email list – remove invalid addresses and re-verify contacts to avoid further damage to your sender reputation.
If you notice ISP throttling or blocks during your ramp-up, don’t push forward. Instead, hold your current volume or roll back to a safer level until your metrics stabilize. Ignoring these issues can make things worse.
For declining open rates, focus on your most engaged recipients – those who recently opened or clicked on your emails. This approach helps rebuild positive engagement signals with ISPs. Additionally, consider implementing a sunsetting policy to reduce email frequency or remove recipients who haven’t interacted in 30–90 days.
Use feedback tools to identify problematic content that might be causing issues.
Finally, set up automated alerts to notify you whenever metrics fall outside acceptable thresholds. This allows you to address problems within hours, protecting your sender reputation. Just like gradual scaling helps build trust, continuous adjustments based on data ensure your emails stay in the inbox where they belong.
Step 5: Prioritize List Quality
Once you’ve established your warmup process, sending limits, and domain rotation, it’s time to focus on the bedrock of email marketing: list quality. Even the most sophisticated infrastructure can’t make up for a list filled with disengaged or irrelevant contacts.
Did you know email lists decay by 22% every year? Poor list hygiene can reduce your effectiveness by as much as 30–40%. Despite this, email marketing remains incredibly effective, delivering a return of $36 to $42 for every $1 spent. But here’s the catch – it only works if you’re reaching people who actually care about your message.
How Engagement Affects Deliverability
Your email’s performance – opens, clicks, replies, and forwards – tells providers whether your messages are welcome or unwelcome. Low engagement signals spam, and when that happens, email providers might throttle your sends, send your emails straight to spam folders, or block them entirely.
Providers are now looking at deeper engagement metrics too, like whether recipients scroll to the bottom of an email or move it to a specific folder. If your unique open rates drop below 5% at a single inbox provider, it’s a warning sign to slow down and refocus on engaged users. Even a spam complaint rate as low as 0.08% can hurt your deliverability.
To manage engagement effectively, consider breaking your list into tiers:
| Engagement Tier | Last Activity | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Engaged | < 1 month | Primary target for all campaigns. |
| Under-engaged | 1–3 months | Send highly relevant win-back content. |
| Uninterested | 3–6 months | Reduce frequency to avoid spam complaints. |
| Unengaged | 6+ months | Remove from active lists to avoid bounces or traps. |
The most powerful engagement signal? A reply. When someone responds to your email, it tells mailbox providers that you’re a legitimate sender. To encourage replies, use low-commitment calls-to-action (CTAs), like asking, "Can I send you a one-pager?" instead of requesting a 15-minute meeting.
A well-maintained, high-engagement list not only improves deliverability but also allows for more precise segmentation.
How to Segment Your Contact Lists
Segmentation turns a generic email list into targeted groups that actually care about what you’re sending. Instead of sending one-size-fits-all emails, you can tailor content to match specific interests and behaviors.
Start by focusing on engagement-based segmentation. Divide your list into categories like "Active Champions" (frequent engagers), "Regular Engagers", "Recovery Candidates" (quiet for 3–6 months), and "Critical Risk" (no engagement in 6+ months). When you’re scaling up, always prioritize sending to your most engaged segments first. This generates positive signals for mailbox providers and protects your sender reputation.
Next, use activity cohorts. For example, target subscribers who’ve opened or clicked an email in the last 30–90 days. For cold outreach, segment by industry, job role, or buyer persona. This makes it easier to personalize your emails based on their unique challenges and interests. Want to stand out? Use subject lines that show you’ve done your homework, like referencing their company or industry.
Don’t overlook traffic separation. Assign specific subdomains for different email types – like t.yourdomain.com for transactional emails (password resets, receipts) and m.yourdomain.com for marketing emails (newsletters, promotions). This way, engagement issues with marketing emails won’t impact the delivery of critical transactional emails.
Finally, set up a preference center. Let subscribers choose how often they want to hear from you (daily, weekly, monthly) and what topics they’re interested in. Giving users control helps reduce unsubscribes and spam complaints.
To keep your list clean over time, adopt a sunsetting policy. Remove or reduce sends to contacts who’ve been inactive for 90 days. Use real-time verification tools to catch typos (like "gmall.com" instead of "gmail.com") and block disposable domains. Adding reCAPTCHA to your signup forms can also prevent bots from filling your list with fake addresses.
"Rather than bringing over an old list, buying a list from someone, or scraping email addresses off social networks, senders need to create opportunities for people to provide their email addresses legitimately." – Ashley Ortiz, Senior Email Delivery Consultant at Twilio SendGrid
Building a quality list might take more time than buying one, but it’s the only way to scale sustainably. Combine engaged contacts with the infrastructure and monitoring you’ve already set up, and you’ll create a system built for growth without compromising deliverability.
Conclusion
Scaling email volume isn’t about sending as many emails as possible – it’s about building trust, both with your audience and mailbox providers. A gradual warmup, consistent sending patterns, and authentic engagement are key to maintaining that trust. Teams that rush the process or neglect proper setup often see their deliverability rates plummet – from 95% to below 50% – within just three to six months of scaling.
The five steps outlined here – warming up mailboxes, setting daily limits, spreading volume across domains, tracking performance, and focusing on list quality – work together seamlessly. Following these practices helps keep hard bounce rates under 1%, minimizes spam complaints, and ensures your emails reach the people who are most likely to engage with them.
Every aspect, from mailbox warmup to performance tracking, is designed to improve deliverability while avoiding common pitfalls. While technical aspects like SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and domain rotation can feel overwhelming, tools like Zapmail simplify the process. Zapmail automates DNS setup, provides pre-warmed Google and Microsoft mailboxes, and isolates domains to protect your brand. What used to take hours can now be done in minutes, freeing you up to focus on what truly matters – creating emails that spark responses.
FAQs
What metrics should I track to safely increase email sending volume?
When increasing your email sending volume, keeping an eye on specific metrics is essential to maintain high deliverability and avoid getting flagged by spam filters. Here’s what to focus on:
- Inbox placement rate: This should be at least 90%, ensuring that the majority of your emails land in recipients’ inboxes instead of their spam folders.
- Bounce rate: Keep this under 2% to protect your sender reputation and prevent email providers from penalizing you.
- Spam complaint rate: Aim to keep this between 0.1% and 0.3%. Higher rates may lead to your emails being flagged or blocked entirely.
- Engagement metrics: Monitor open rates, click-through rates, and unsubscribe rates. These indicators reveal how interested your audience is and help you fine-tune your strategy.
By staying on top of these metrics, you can grow your email campaigns without compromising your sender reputation or losing audience engagement.
What are the benefits of using pre-warmed mailboxes for email outreach?
Using pre-warmed mailboxes can give your email outreach a head start by establishing a strong sender reputation right from the beginning. When new mailboxes send a high volume of emails too quickly, providers like Gmail or Outlook often flag them as suspicious. Pre-warmed mailboxes, however, come with a track record of steady, high-quality email activity, reducing the risk of being flagged.
With tools like Zapmail, you can access pre-warmed Google and Microsoft mailboxes that are ready to go, offering optimized deliverability without the hassle of manual warm-up. This ensures your emails are more likely to reach inboxes rather than getting lost in spam folders. Plus, features such as automated DNS setup, domain isolation, and seamless platform integrations make it easier to scale your campaigns while keeping them reliable and efficient.
Why is it important to maintain a high-quality email list for deliverability?
Maintaining a well-managed email list is crucial for ensuring your emails actually make it to your audience’s inboxes. It helps minimize hard bounces, steer clear of spam traps, and safeguard your sender reputation – all of which play a big role in keeping your emails out of spam folders.
A tidy email list means you’re connecting with engaged recipients who are more likely to open, read, and interact with your messages. This not only boosts your campaign performance but also improves your email deliverability. Taking the time to regularly update and verify your list can have a noticeable impact on the success of your email outreach efforts.